Digital Health’s Role in Improving Patient Engagement


In recent years, the patient journey has become more virtual, with patients seeking online information prior to engaging with healthcare providers (HCPs). Even as we transition back into traditional, in-person patient care, digital health is proving to be much more than just a trendy fad—it’s a movement that is here to stay. So how can digital health improve patient engagement, and why is it important?
What Is Digital Health?
Digital health is the use of technology platforms in healthcare to communicate medical information; track, prevent, manage, and treat diseases; and promote health and wellness. It covers many different categories within patient care, including health information technology, mHealth (otherwise known as mobile health), wearable devices, telehealth, and telemedicine. There are many different kinds of digital health tools, including:
- Patient portals
- Biometric sensors
- Wearables
- Virtual physician visits
- Care emails and text messages
- Digital billing and wallets
- Electronic health records (EHRs)
- Social media
- Imaging
While digital health’s rapid implementation was in part due to COVID-19, many organizations were investing in these innovative technologies long before the pandemic began in order to better engage patients globally.
The Impact of Digital Health Tools on Patient Engagement
According to the CDC, a growing amount of evidence shows that the more engaged a patient is, the more likely the patient is to have better health outcomes and experiences in their health journey. In trying to understand the patient perspective, healthcare providers are better positioned to relay information to the patient in a way that enhances their understanding of their illness and treatment options, fosters trust, and develops lasting positive relationships not only with the patient but also their community and support system.
Digital health enables HCPs to efficiently connect and communicate with patients in a way that is tailored to the patient’s preference. These tools also help monitor and treat varying ailments and illnesses in a way that’s typically less invasive and offers the patient more control. This type of care is often described as “patient-centric care.”
In addition to improving the patient experience, digital health technologies also widen access to healthcare for underserved communities. For example, for patients who live in rural areas that are inaccessible or far away from physicians’ offices, these tools can enable remote access to these patients and ensure they are still receiving high-quality care.
Beyond location, there are other factors that can limit access to adequate healthcare. A patient’s age, ethnicity, language, socioeconomic status, and gender (just to name a few) must all be taken into account when developing technologies to ensure all populations have equitable access to health information.
As another example, a 2020 Accenture report, which surveyed over 2,000 consumers across several countries, found that younger patients were more open to virtual care than traditional in-person care.
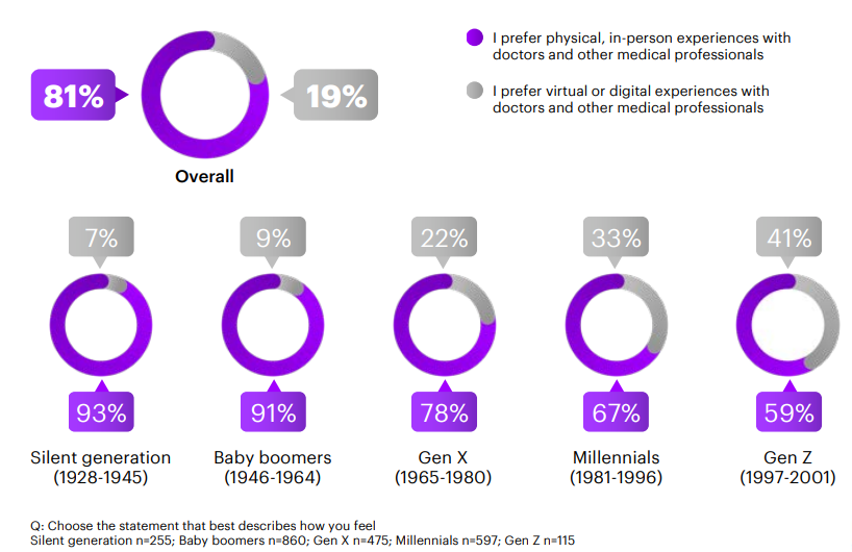
Figure 1: https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insights/health/leaders-make-recent-digital-health-gains-last
Based on this data, if an HCP is considering a digital health platform that would enable their patient to meet with them virtually, they’d likely recommend it to a younger patient rather than someone more senior.
Four Considerations for Improving Patient Engagement when Introducing Digital Health Platforms
As the digital health space continues to innovate new ways to better reach, serve, support, and engage patients, life sciences organizations must also continue to improve the ways these tools are introduced to and utilized by patients and HCPs. While there are several considerations to take into account depending on where the digital solution is being marketed to ensure compliance and oversight, here are four universal components to consider, regardless of region:
1) Patient-Centric Design
One of the biggest keys to a successful digital patient engagement tool is designing it with the patients in mind. The less user-friendly an interface is, the less likely patients are to use it. It’s imperative to understand the local market, including patient preferences and current pain points to ensure the tool’s efficacy and consistent, long-term use.
2) Omnichannel Strategy
Meet your patients where they are. With so many different types of digital health tools that exist and are continuing to be developed, it’s important to cater to patients’ preferences. While one patient may prefer email messaging to learn about new treatment options, another patient may prefer to engage in a social media campaign. Be flexible in your approach to sharing relevant health information with patients, and ensure the information, regardless of where it’s accessed, is consistent.
3) Multilingual and Cultural Adaption
Particularly important for global companies operating across diverse regions and cultures, consider the translation and localization of important health information to limited English proficiency (LEP) [SG1] or non-English-speaking patients. High-quality, certified translations can help improve health literacy, engage a wider group of patients, and empower the public to take control of their health.
4) Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Beyond language considerations, it’s important to also consider all populations, including those of diverse backgrounds, when developing or marketing your digital health tool. It’s imperative to test your technology not only for its usability, but also for its accessibility for those with disabilities. In one study, a literature search of 5,968 sources across five databases found that only 25 digital health technologies met inclusion criteria. Text size, fonts, colors, ease of use, and guidelines and regulations such as WCAG 2.0 are all critical components for ensuring your digital health tool is equitable for all, regardless of ethnicity, disability, location, language spoken, age, etc.
Digital health is here to stay. As the patient journey continually becomes more personalized to improve patient engagement and health outcomes, digital health platforms enable HCPs to not only tailor patient care, but also reach a broader group of patients.
If you missed our previous blog on specific considerations for implementing digital health therapeutics in China, you can check it out here. Interested in learning more about our digital patient engagement solutions? Drop us a line today!



